Wiradjuri country
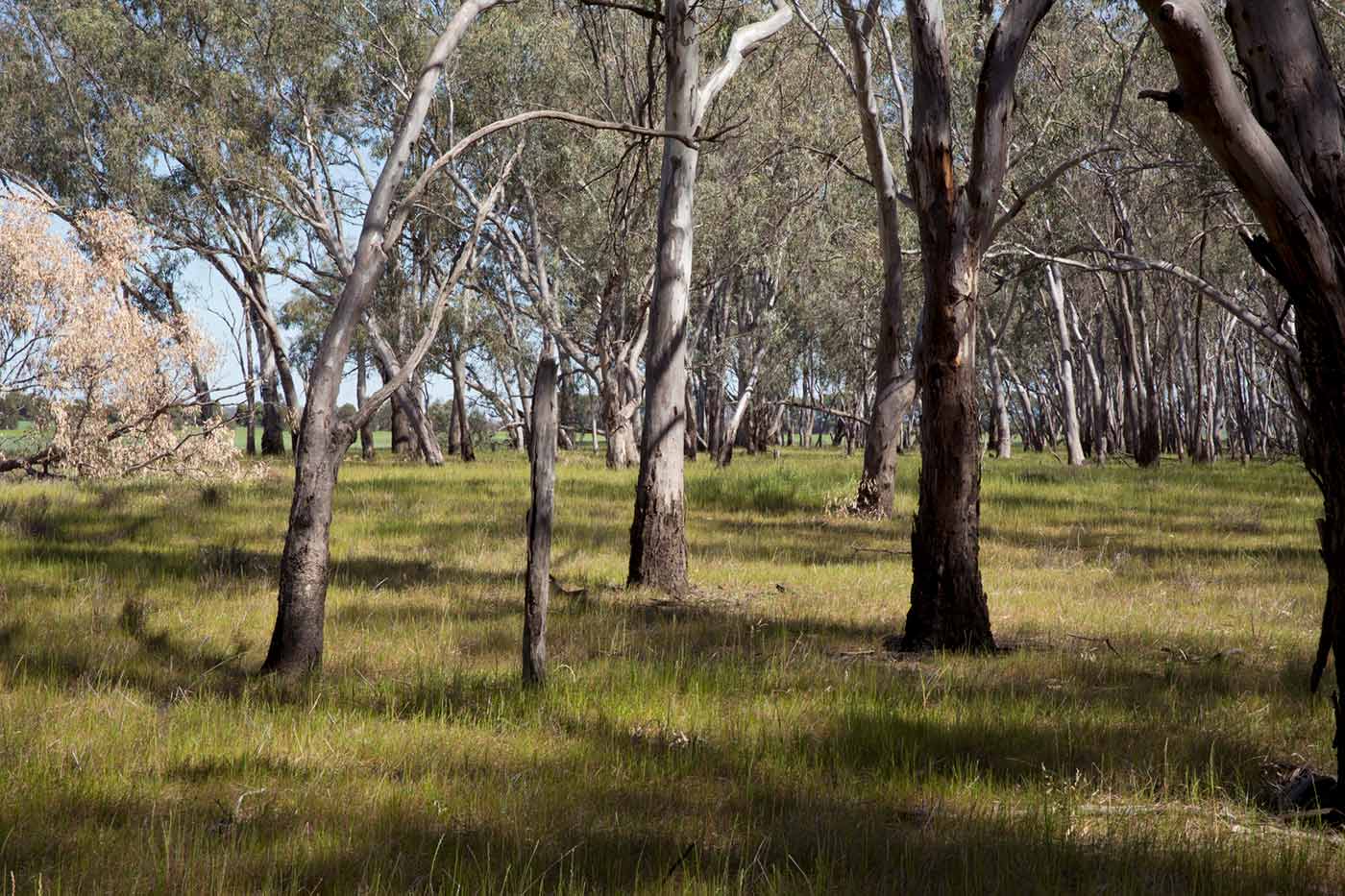
Wiradjuri country includes large areas of present day New South Wales. Wiradjuri guides assisted explorer Thomas Mitchell on his expeditions through their country.
Explore the relationship between Mitchell and his guides and how Wiradjuri culture lives on today through art and community engagement.
Setting the scene
Uncle Stan Grant, Wiradjuri elder, 2014:
I think it’s pretty important … that we respect our land and we respect the people coming onto it. And, of course, the people have got to respect … the people from the land.
The Wiradjuri are the people of the three rivers: the Lachlan, the Macquarie and the Murrumbidgee. In the 1830s colonists claimed vast areas of their country in south-west New South Wales.
Surveyor Thomas Mitchell travelled through Wiradjuri country at this time. There was sporadic violence between Mitchell’s party and Wiradjuri people. But Mitchell was helped by Wiradjuri guides, including John Piper and Turandurey. They often negotiated his safe passage and shared their knowledge of country.
Thomas Mitchell, journal entry, 1836:
In most of our difficulties by flood and field, the intelligence and skill of our sable friends made the ‘white-fellows’ appear rather stupid. They could read traces on the earth, climb trees, or dive into the water, better than the ablest of us.
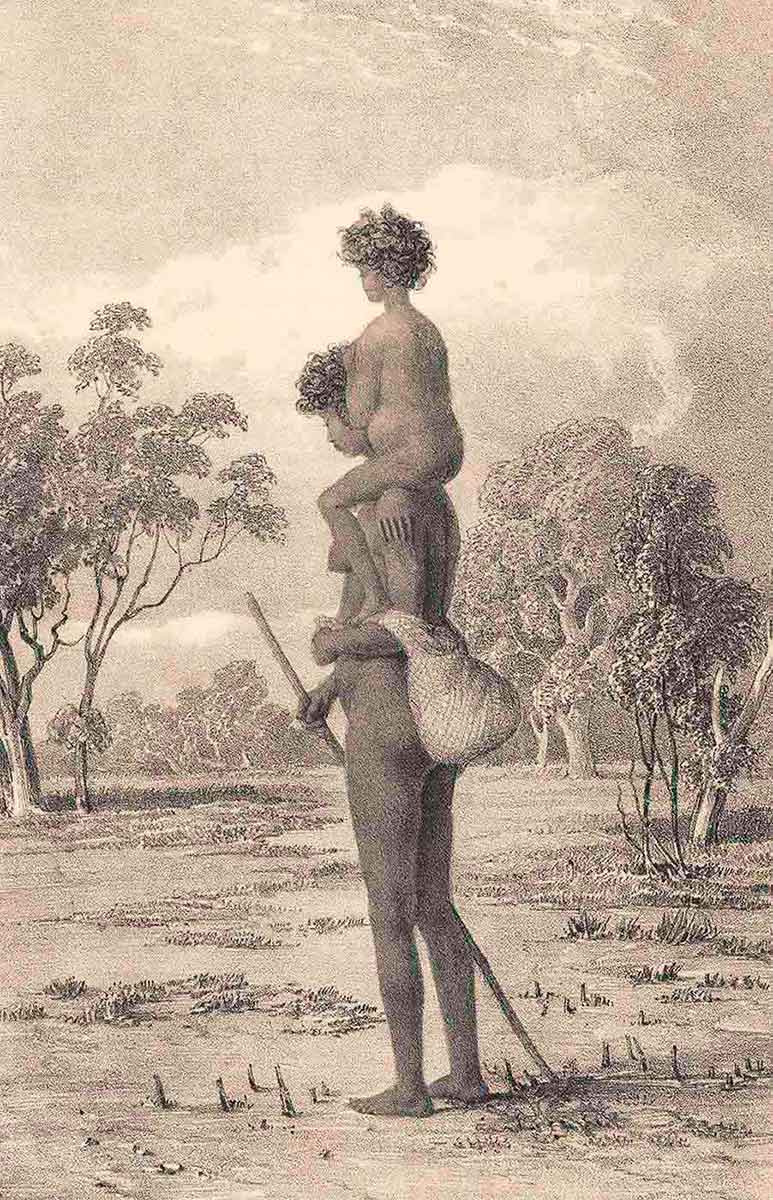

Turandurey and her daughter
Thomas Mitchell, journal, 7 May 1836:
Formality was maintained very remarkably by the old man and Piper ... each stood silent for a full quarter of an hour about eight yards apart, neither looking at the other ... [Turandurey] however became the intermediate channel of communication, for both spoke alternately in a low tone to her. At length Piper addressed the old man, raising his voice a little but with his head averted; and the other answered him in the same way; until at length by slow degrees they got into conversation. We were then informed that water was to be found a mile or two on, and the old man agreed to guide overseer Burnett and Piper to the place.
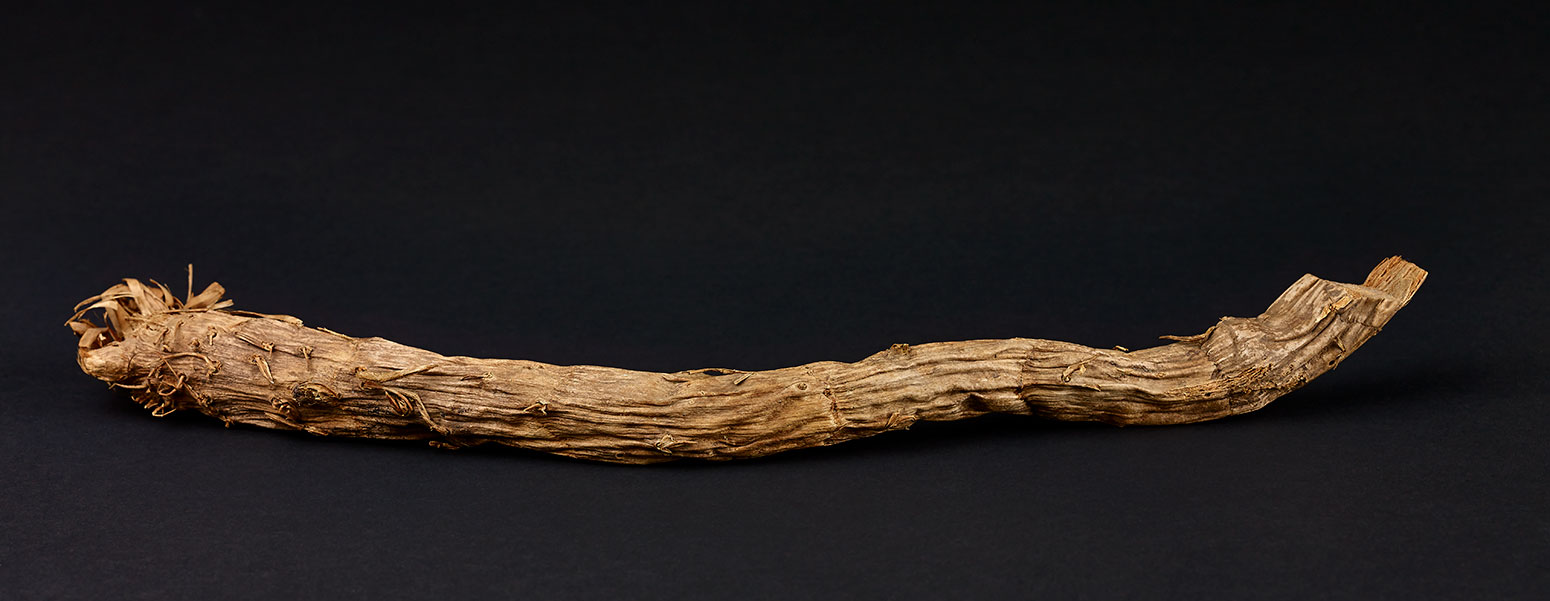
Balyan (bulrush root)
Thomas Mitchell collected a number of objects during his expeditions, including a sample of balyan, one of the main foods of the Wiradjuri people.
Thomas Mitchell, journal, 2 May 1836:
The principal food of these inhabitants of the Kalare [Galari] or Lachlan appeared to be balyan, the rhizome [root-like stem of the plant] ... of a ... bulrush growing amongst the reeds. This contains so much gluten, that one of our party [Charles Webb], made in a short time some excellent cakes of it, and they seemed to me lighter and sweeter than those prepared from common flour.
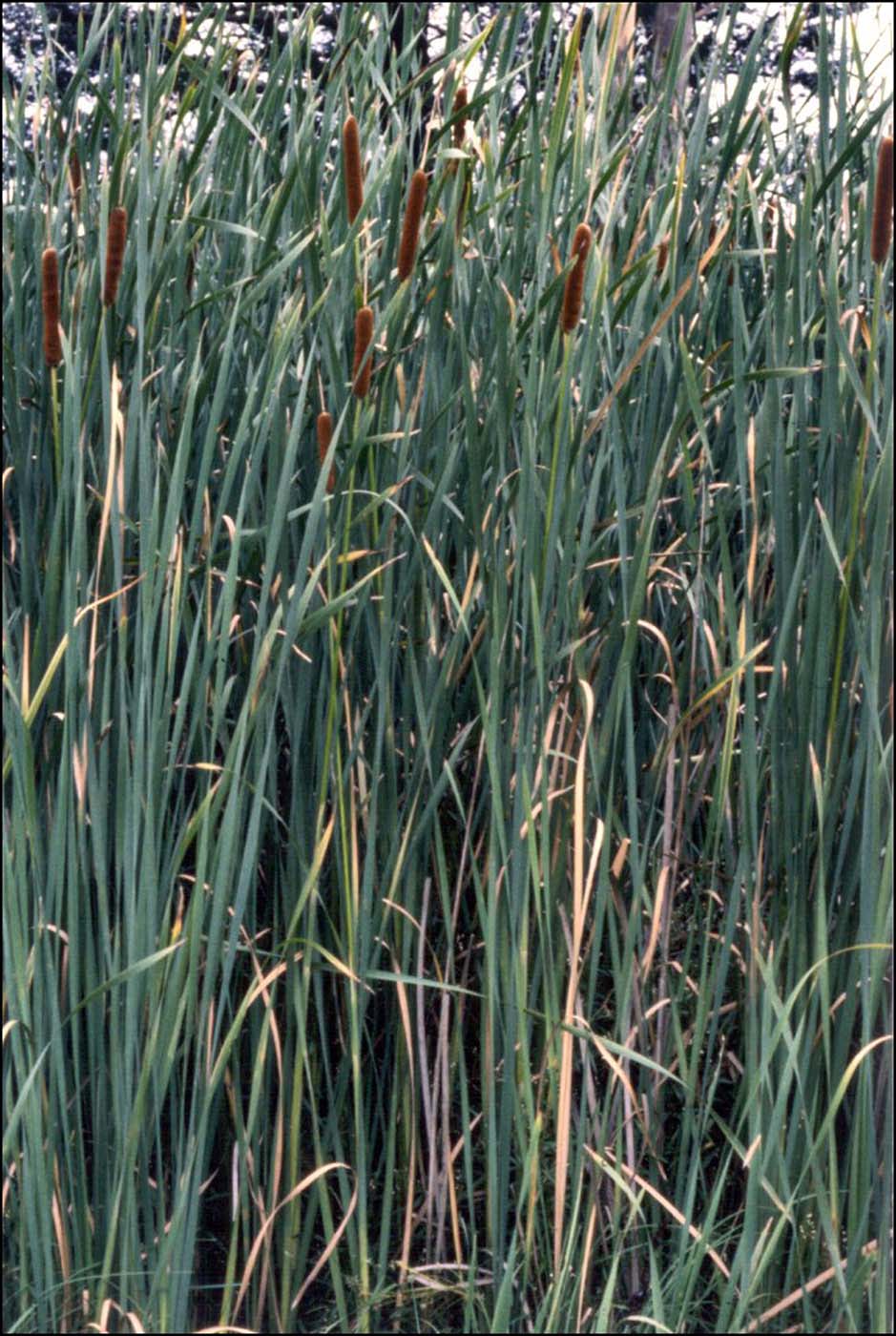
Balyan (bulrush plant)
Apart from using the root of the bulrush for food, the plant provided fibre for making string, baskets and nets.
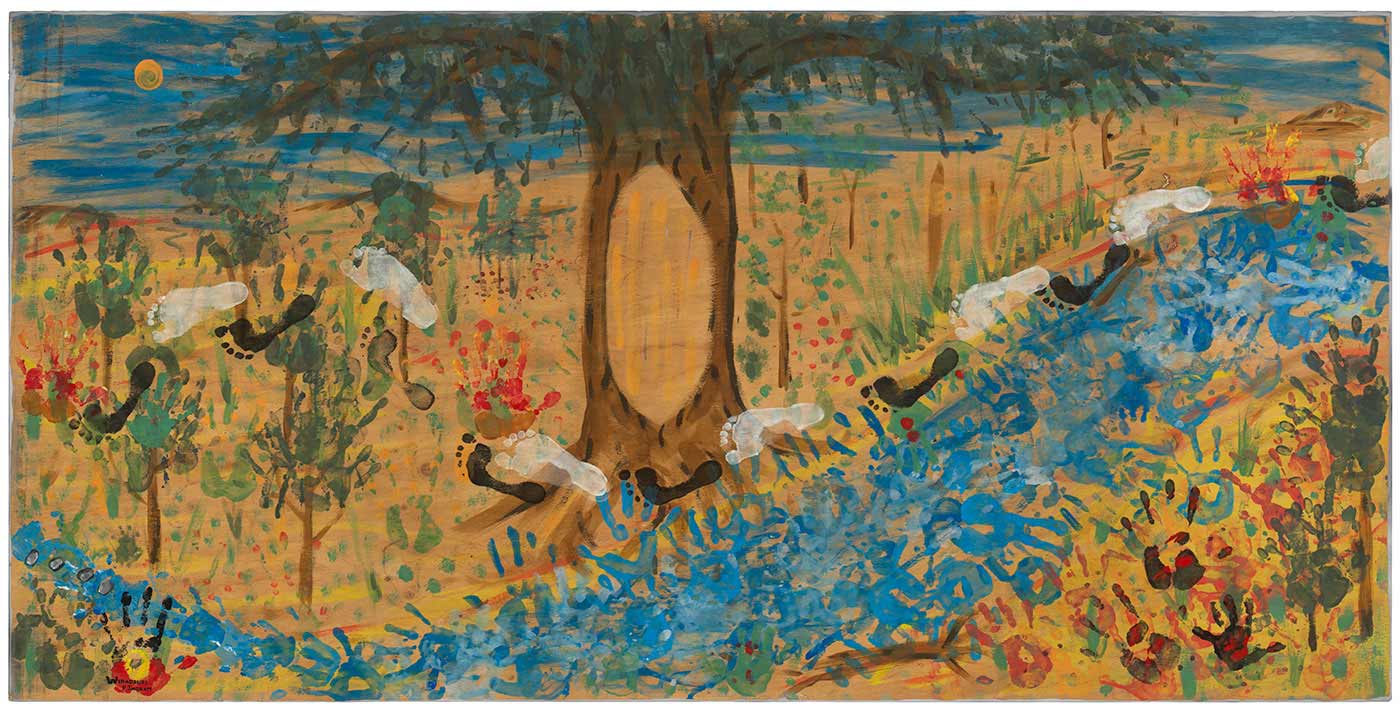
Yanhanha Murruway (Walking Path)
In 2014 a group of people embarked on a three-day trek, walking through Wiradjuri country from Buckingbong to Birrego, camping along the way. As they walked, they explored Aboriginal and settler histories, including those of frontier violence. It was a journey of healing for many of the participants, both Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal.
During the walk, Wiradjuri artist Peter Ingram collaborated with fellow walkers to create this artwork, Yanhanha Murruway, which tells the story of the journey as each day unfolded.

Peter Ingram, Wiradjuri man, 2015:
Yanhanha Murruway [means] ‘walking path’ in Wiradjuri ... It’s about how we are still keeping our art alive in contemporary times, moving forward together ... acknowledging and understanding our history ... We can’t change yesterday but we can make a better tomorrow.
What do you know about Wiradjuri country?
More activities
The Buckingbong to Birrego walk was a journey of healing for many of the participants. It inspired the painting above. You can read more in the Buckingbong to Birrego ebook on the Issue website.
There are different ways communities can remember and heal; ceremonies, monuments and events like this walk are a few examples. Do some research to see if you can you find other examples of healing or commemorative walks. Think about your local community. In what ways does your community remember and honour the past?
Investigate the balyan that Thomas Mitchell writes about in his journal. It is also known as bulrush plant or Typha. Find out where it grows and how Aboriginal people prepared it for eating. What other uses did this plant provide? These resources may help your research:
- Flora of Australia online
 'Aboriginal plant use in south-eastern Australia' (PDF 1.7mb) from the Parks Australia website
'Aboriginal plant use in south-eastern Australia' (PDF 1.7mb) from the Parks Australia website
Watch the video, Our Mother Tongue: Wiradjuri on the ICTV website. Why do you think it is important that Aboriginal languages continue to be learned and used? How many languages do you speak? What are they? What Aboriginal languages are spoken in the region where you live?
Explore more on Community stories



